A tractor is a wheeled or tracked vehicle used in agriculture, construction and industrial fields. Tractors consist of basic elements such as an engine, chassis, tires or tracks and a control console. Tractors generally have large and powerful engines that provide towing power for other vehicles or machines through power drivetrains.
What is a Tractor?
Tractors used for agricultural activities are used in conjunction with many different agricultural implements for soil cultivation, planting, harvesting and other operations. Tractors used for construction and industrial activities are used for towing and operating machines used for carrying loads, digging, leveling and other operations.
Tractor play an important role in the agricultural and industrial sectors, making them indispensable vehicles in the modern world.
How Does a Tractor Work?
The working principle of tractors essentially involves transmitting the power of the engine to the wheels or tracks through power transmission components. Heart of a tractor is its engine and diesel engines are generally used in tractors.
The engine converts the energy obtained by compressing and igniting the fuel-air mixture into mechanical motion. This motion is transmitted from the engine's output shaft to the power transmission components.
Tractor control is achieved through the control console in the driver's cabin. The control console contains parts such as the accelerator pedal, brake pedal, clutch pedal, steering wheel, gear lever, and other control buttons.
Power transmission components in tractors generally consist of parts such as a hydraulic pump, clutch, transmission, rear axle, front axle and differential. These components come together to transmit power and motion to the wheels or tracks.
A tractor's movement is typically provided by the rear wheels or tracks. Power controls the rotation of the wheels through the differential. Accessories such as a tow ring or tow bar attached to the rear axle allow the tractor to pull another vehicle or move machinery.
In short, tractors move thanks to their powerful engines and power transmission components and are used in various operations in the agriculture, construction and industrial sectors.
What is the Engine Structure of Tractors?
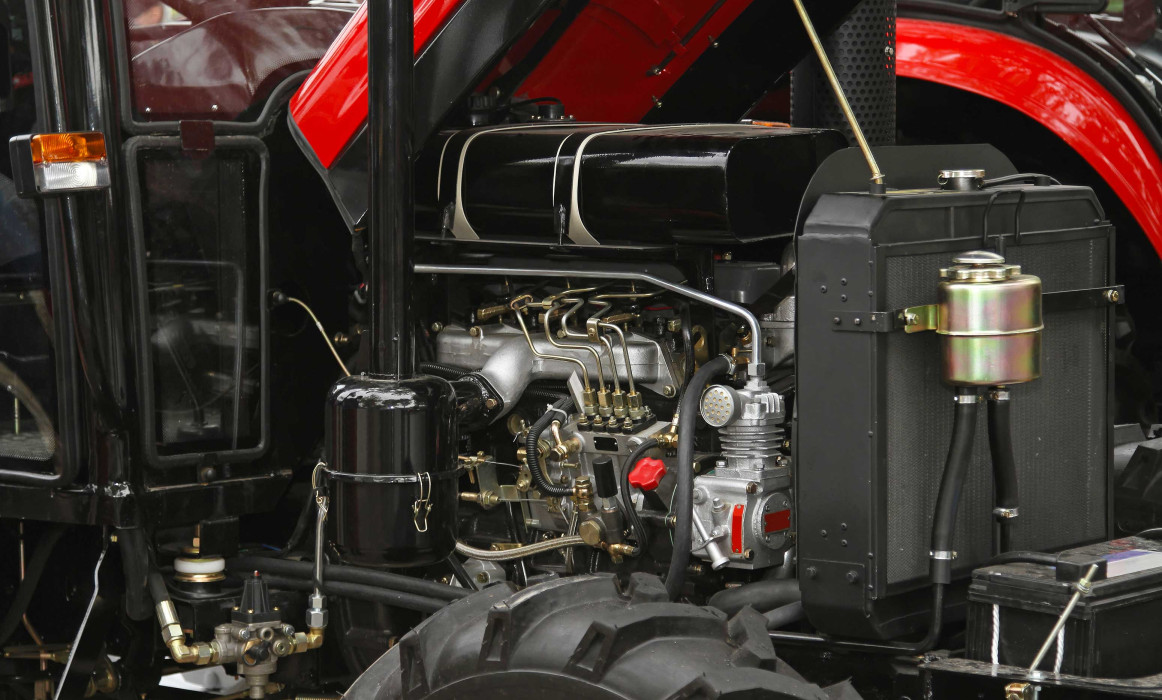
Tractors are typically comprised of diesel engines. These engines produce mechanical motion power through the compression and combustion of fuel. Tractor engines have a complex structure and are designed for high power and durability.
Tractor engines must be high-powered and durable. Therefore, the engine structures are designed accordingly. The engine consists of parts such as the cylinder block, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, fuel system, air system, lubrication system and cooling system.
The cylinder block is the main body of the engine. It is a structure that encompasses the cylinders within the engine. The cylinders can range from 4 to 12 in number. Pistons move within the cylinders, compressing the combustion chamber. The cylinder head covers the top of the cylinders, providing a seal with the cylinder head gasket.
Pistons compress the combustion chamber by moving inside the cylinders to generate power. They move through connecting rods attached to the crankshaft, which converts the piston movements into rotational motion to transfer power to the transmission system.
The tractor fuel system is designed to meet the engine's fuel needs. This system draws fuel from the tank and sends it to the combustion chambers through the fuel pump. The air system is designed to meet the engine's air needs. This system draws clean air through the air filter and sends it into the cylinders.
The lubrication system is designed to reduce wear and friction on engine parts. This system pumps clean oil to the engine parts through the oil filter. The cooling system regulates the engine's temperature by cooling it with coolant or air.
 en
en  tr
tr